Special: Swiss tax reform STAF: R&D Instruments 2024
STAF R&D instruments
The Tax Reform and AHV financing (or TRAF), which came into force at the federal level on January 1, 2020, is the most important Swiss tax reform in decades and has significantly changed the Swiss tax landscape. The vast majority of cantons has already fully implemented the TRAF. Among other things, the reform introduced instruments to provide tax benefits for research and development activities (TRAF R&D instruments). These internationally accepted tax instruments serve to promote innovation activity. The BAK Taxation Index project has analysed the impact of the STAF R&D instruments on the EATR (i.e., the effective average tax rate) for companies.
EATR when using the STAF R&D instruments 2024
The STAF R&D instruments significantly reduce the tax burden for research-intensive companies in the Swiss cantons. At the same time, the flexible implementation in the cantons changes the Swiss ranking. Although the ranking is led by Central and Eastern Switzerland, cantons such as Bern and Zurich (which traditionally belong to the high-tax cantons) make up several ranks in the case of very research-intensive companies.

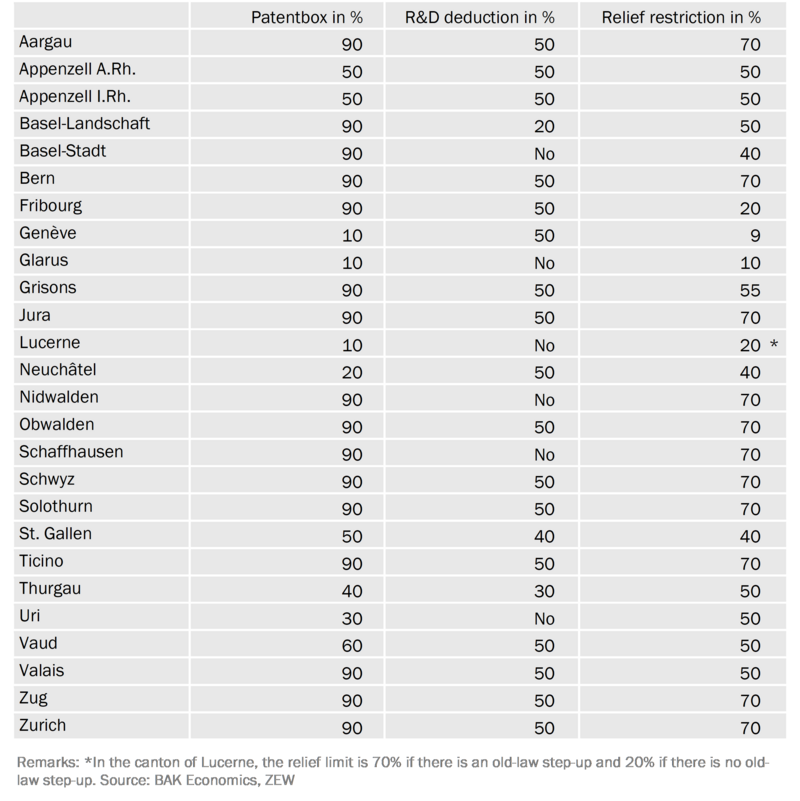
Methodology
The BAK Taxation Index for companies measures the effective average tax rate (EATR) for companies in all 26 cantons and their main international competitor locations. It includes all types of taxes and regulations relevant to investors at the various levels of government.
The BAK Research Intensive Companies Model was developed within the framework of the project BAK Taxation Index to calculate the effective average tax rate (EATR) when using the newly introduced STAF (or TRAF) R&D instruments (patent box, R&D deduction, incl. relief limitation). The main difference to the standard model of the BAK Taxation Index is that not an acquired but a self-created intangible asset (patent) is assumed. The tax burden when using the STAF R&D instruments was calculated for three different types of investments or companies, which differ in their research intensity:
|